When it comes to electronics and DIY projects, a soldering iron is one of the most essential tools in your kit. But even the best soldering iron is only as good as the tips you use with it. Understanding the different types of soldering iron tips, iron soldering tips, and how to maintain your iron soldering iron can significantly improve your soldering skills. In this blog, we’ll dive into the world of soldering tips, helping you choose the right ones for your projects and ensuring you get the most out of your soldering iron.
Soldering Iron Tips: The Basics
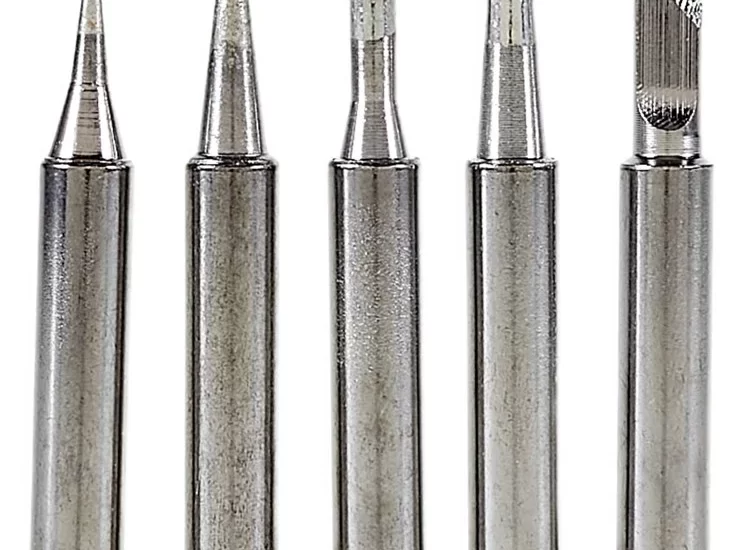
Soldering iron tips are the interchangeable components at the end of a soldering iron that transfer heat to the soldering surface. These tips come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific types of soldering tasks. Here’s a look at some of the most common soldering iron tips:
Conical Tips: Conical tips are pointed and are ideal for precision work. They’re great for soldering small components on a circuit board because they allow you to focus heat on a tiny area.
Chisel Tips: Chisel tips are flat and wide, making them perfect for soldering wires or larger components. The broad surface area allows for better heat transfer, which is crucial for effective soldering on larger surfaces.
Bevel Tips: Bevel tips have a slanted surface and are versatile enough to handle both precision work and larger tasks. They’re particularly useful for dragging solder across multiple connections.
Knife Tips: Knife tips are sharp and angled, ideal for cutting through solder or for soldering in tight spaces where other tips might not reach.
Iron Soldering Tips: Choosing the Right One
Selecting the correct iron soldering tip depends on the specific job you need to do. Here are some factors to consider:
Size of the Components: If you’re working with tiny components, such as those on a PCB (printed circuit board), a conical or fine chisel tip will be more appropriate. For larger components, a wider chisel or bevel tip will be more effective.
Type of Solder: Different types of solder (lead-based, lead-free, etc.) require different levels of heat. Ensure that your soldering tip can handle the required temperature without degrading.
Precision: For tasks requiring high precision, such as micro-soldering, a fine tip is necessary. For less precise work, a broader tip will be more efficient and provide better heat transfer.
Durability: Some tips are coated with special materials like iron or nickel to prolong their lifespan. If you’re soldering frequently, investing in durable tips can save you money and time in the long run.
Maintaining Your Iron Soldering Iron
No matter how good your soldering tips are, they won’t perform well if your iron soldering iron isn’t properly maintained. Here are some maintenance tips to keep your soldering iron in top condition:
Clean the Tip Regularly: After each use, clean your soldering tip with a damp sponge or a brass wire cleaner to remove any oxidized solder. This helps maintain efficient heat transfer and prolongs the life of the tip.
Tinning the Tip: Tinning involves coating the soldering tip with a thin layer of solder before and after use. This prevents oxidation and ensures good heat conductivity for the next use.
Use the Right Temperature: Using too high a temperature can damage both your soldering iron and the components you’re working on. Always adjust the temperature to the appropriate level for the solder and materials you’re using.
Store Properly: When not in use, store your soldering iron in a safe place where the tip is protected from damage. Using a stand with a sponge or a holder that keeps the tip off surfaces is ideal.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of soldering iron tips and understanding how to care for your iron soldering iron can elevate your DIY electronics projects from good to great. By selecting the right tip for each job, maintaining your tools properly, and following best practices, you’ll achieve better solder joints and extend the lifespan of your equipment. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, the right knowledge and tools are key to success in soldering.